Berber Culture: A Journey through History and Tradition
Table of Contents

Introduction to Berber culture:
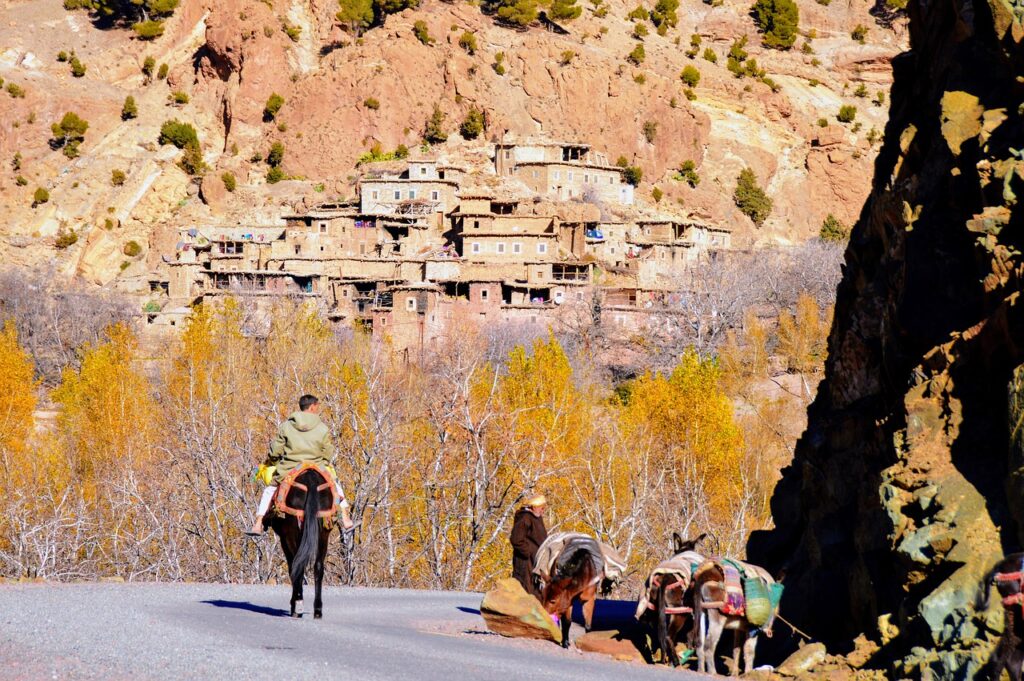
Nestled in the heart of North Africa, the Berber people have cultivated a rich heritage spanning millennia. This ancient Berber Culture, marked by resilience and adaptability, thrives amidst some of the world’s most diverse and challenging landscapes.
Origins and Migration:
The Berber people, also known as Amazigh, form the indigenous inhabitants of North Africa. Their history dates back to ancient times, predating the Arab and European influences that would later shape the region. While scholars continue to debate their exact origins, it is widely accepted that they descend from the early inhabitants of the Maghreb.
Language and Script:
A pivotal aspect of Berber identity lies in their distinctive language. Spoken by millions across North Africa, the Berber languages, part of the Afro-Asiatic family, encompass a variety of dialects associated with specific regions and communities. Recent efforts have been made to preserve and promote Berber languages, including initiatives for standardized written forms. The Tifinagh script, with its millennia-old history, lies at the core of Berber linguistic identity and is currently experiencing a revival.
Cultural Traditions:
Berber culture boasts a diverse tapestry of traditions, each reflecting the unique stories and significance of its communities.
Music and Dance:
Berber music, characterized by haunting melodies and rhythmic beats, utilizes traditional instruments like the bendir and the gimbri. These instruments play a vital role, providing the backdrop for lyrical tales of love, nature, and daily life. Berber dance forms like Ahwach and Ahidus hold a central place in celebrations and festivals, evoking unity and communal spirit.
Clothing and Adornments:
Berber attire combines practicality with artistic expression. Women often don colorful garments adorned with intricate geometric patterns, signifying a profound connection with nature. The use of silver jewelry, including fibulae, bracelets, and necklaces, serves not only as personal adornment but also holds cultural and social significance.
Cuisine:
Berber dishes embody a rich culinary heritage deeply rooted in tradition and local ingredients. Popular dishes include couscous, tagines, and savory meat stews infused with an array of aromatic spices, creating a delightful gastronomic experience unique to Berber culture.
Modern Resurgence and Cultural Preservation:
In recent years, the Berber culture has experienced a dynamic revival that bridges ancient traditions with contemporary innovations. Across North Africa, young generations are reinvigorating a legacy that has withstood centuries of change. Today, Berber culture symbolizes resilience and creative adaptation in the face of rapid globalization. Initiatives focused on preserving indigenous language, art, and craftsmanship now merge with modern digital platforms to promote cultural exchange and learning. Educational programs in schools and community centers emphasize the importance of the Berber language, the Tifinagh script, and time-honored storytelling, ensuring that ancestral wisdom endures for future generations.
Vibrant festivals and art exhibitions further celebrate Berber culture by drawing local communities and international visitors alike. These events showcase traditional music, dance, and culinary arts while providing a stage for contemporary artists who reinterpret ancient symbols through painting, sculpture, and digital media. Rural artisans continue to produce handwoven textiles, pottery, and silver jewelry using techniques passed down through generations.
Moreover, diaspora communities worldwide play a vital role in keeping Berber culture alive. They organize cultural gatherings, language workshops, and art fairs that reinforce their identity and share their heritage with a global audience. In sum, the modern revival of Berber culture represents a celebration of the past and a forward-looking vision for the future, where tradition and innovation coexist harmoniously. This renewed momentum not only reinforces a deep connection to ancestral heritage but also inspires modern creativity, ensuring that Berber culture continues to flourish globally with great promise.
Conclusion:
The Berber people stand as a testament to the enduring strength of indigenous cultures in the face of centuries of change. Their history, traditions, and languages form a vibrant tapestry that continues to shape the cultural landscape of North Africa.
In a world of rapid globalization, the Berber people remind us of the importance of preserving and celebrating our diverse human heritage. By appreciating the rich tapestry of Berber culture, we gain deeper insights into the complexities and beauty of our shared global history.